Science of Addiction
Fact: Addiction is a chronic and complex brain disease.
What is Drug Addiction?
The National Institute of Drug Abuse (NIDA) defines addiction as a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use, despite harmful consequences.1
Addiction as a brain disease
ADDICTION is treatable and people in recovery from substance use disorder can go on to live healthy, successful, and meaningful lives.
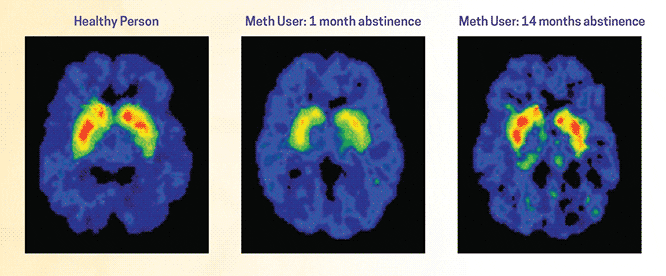
Dopamine’s role in addiction
When we experience pleasure, our brain releases a neurotransmitter called dopamine. Dopamine is important for memory, learning, behavior, and motivation. When someone takes a drug, their brain produces large surges of dopamine – way more than gets produced as a result of a natural, pleasurable behavior like eating, listening to music, creative pursuits, or exercising – this is what makes a person “feel high”. The powerful reward sensation of “feeling high” creates a strong and rapid memory in the brain, associating drug use with extreme feelings of pleasure. With repeated exposure, it diminishes its sensitivity and makes it hard to feel pleasure from anything besides the drug.
The effects of long-term drug use